Water Body Surveyor – Accurate Surveying & Mapping of Water Resources
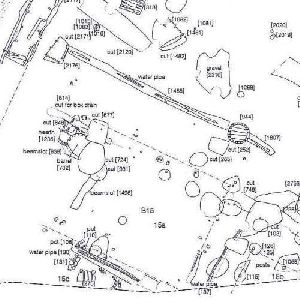
A Water Body Surveyor specializes in surveying and mapping natural and man-made water bodies such as rivers, lakes, ponds, reservoirs, wetlands, and canals. These surveys are essential for water resource management, irrigation projects, flood control, aquaculture, urban planning, and environmental conservation. By providing accurate data on size, depth, boundaries, and storage capacity, water body surveyors help governments, developers, and communities make informed decisions about water usage and sustainability.
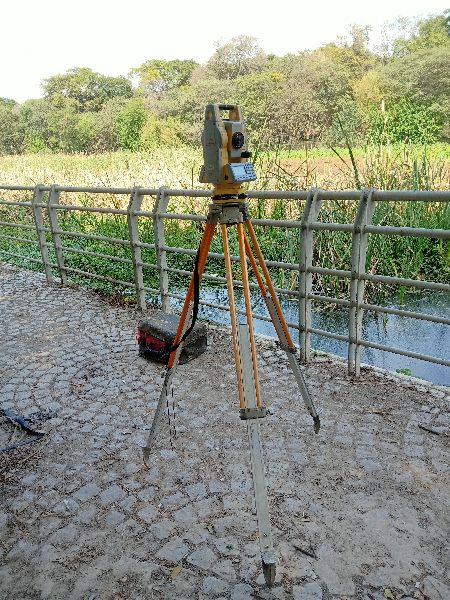
Using advanced technologies like DGPS, Total Station, Drones, Bathymetric Equipment, and GIS Mapping, surveyors capture precise measurements of water spread area, depth profiles, and surrounding topography. This data is further processed into digital maps, 3D models, and CAD drawings for planning, analysis, and legal documentation.
Key Services of a Water Body Surveyor:
Boundary Demarcation: Identifying legal limits of water bodies to prevent encroachment.
Hydrographic & Bathymetric Surveys: Measuring water depths and silt levels.
Capacity Estimation: Calculating storage potential for drinking water, irrigation, or industrial use.
Environmental Monitoring: Assessing siltation, water quality, and ecological balance.
Restoration Planning: Providing technical inputs for desilting, embankment strengthening, and conservation projects.
Looking for "Water Body Surveyor" ?
Explore More Services