Kursi Road, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
- GST NO. : 09KKLPK8365P1ZU
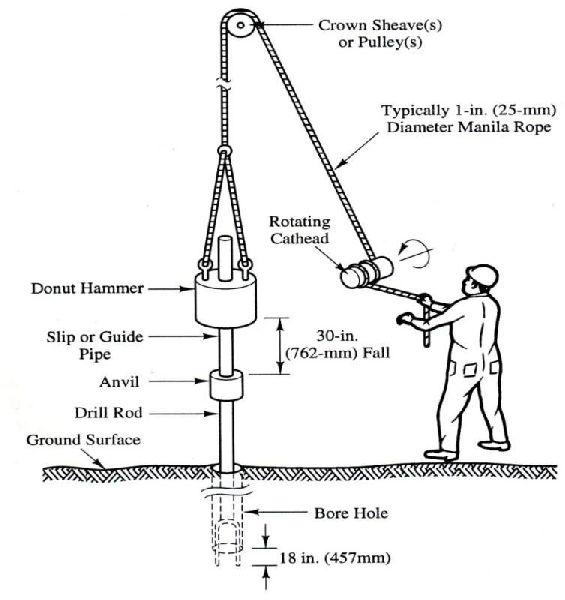
Standard Penetration Test
The Standard Penetration Test (SPT) is a widely used in-situ geotechnical testing method designed to assess the subsurface soil conditions at a specific location. It is commonly employed in the fields of civil engineering, geotechnical engineering, and construction to gather valuable information about soil properties. The test involves driving a standardized sampler into the ground and recording the number of blows required to penetrate the soil to a specified depth.
Key features and steps of the Standard Penetration Test include:
-
Test Apparatus: The primary equipment used in the SPT consists of a split-barrel sampler, a drill rod, a drive hammer, and a tripod setup. The split-barrel sampler is driven into the soil at the test location.
-
Depth Measurement: The test is typically conducted at regular intervals as the drill rod is advanced into the ground. The depth of penetration is recorded to create a profile of soil properties at various depths.
-
Energy Measurement: The energy transferred to the sampler is standardized by the weight of the hammer and the free-fall distance. This helps ensure consistency in the test results.
-
Number of Blows: The number of blows required to achieve a penetration of 12 inches (305 mm) for the first 6 inches (152 mm) and 18 inches (457 mm) for the subsequent 6 inches is recorded. This measurement is known as the "N-value" or "blow count."
-
Soil Sampling: After completing the test at a specific depth, the split-barrel sampler is retrieved, and the soil samples collected are used for further laboratory analysis to determine soil properties such as grain size, moisture content, and cohesion.
-
Data Interpretation: The N-values obtained from the SPT are used to assess the relative density and shear strength of the soil. Engineers and geotechnical professionals analyze the results to make informed decisions regarding foundation design, slope stability, and other geotechnical considerations.
-
Site Characterization: SPT results contribute to the overall site characterization, providing valuable information for construction projects, such as building foundations, bridges, and other infrastructure.
-
Correlations: The N-values can be correlated with soil properties and used to estimate parameters such as the angle of internal friction, cohesion, and bearing capacity.
The Standard Penetration Test is a cost-effective and widely accepted method for assessing subsurface soil conditions. Its simplicity and repeatability make it a valuable tool for geotechnical investigations, helping engineers and construction professionals make informed decisions about the design and construction of structures on a given site.
Looking for "Standard Penetration Test" ?
Explore More Services